Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Advection schemes
Illustrating the difference between Euler and Runge-Kutta propagation schemes, using an idealised (analytical) eddy current field.
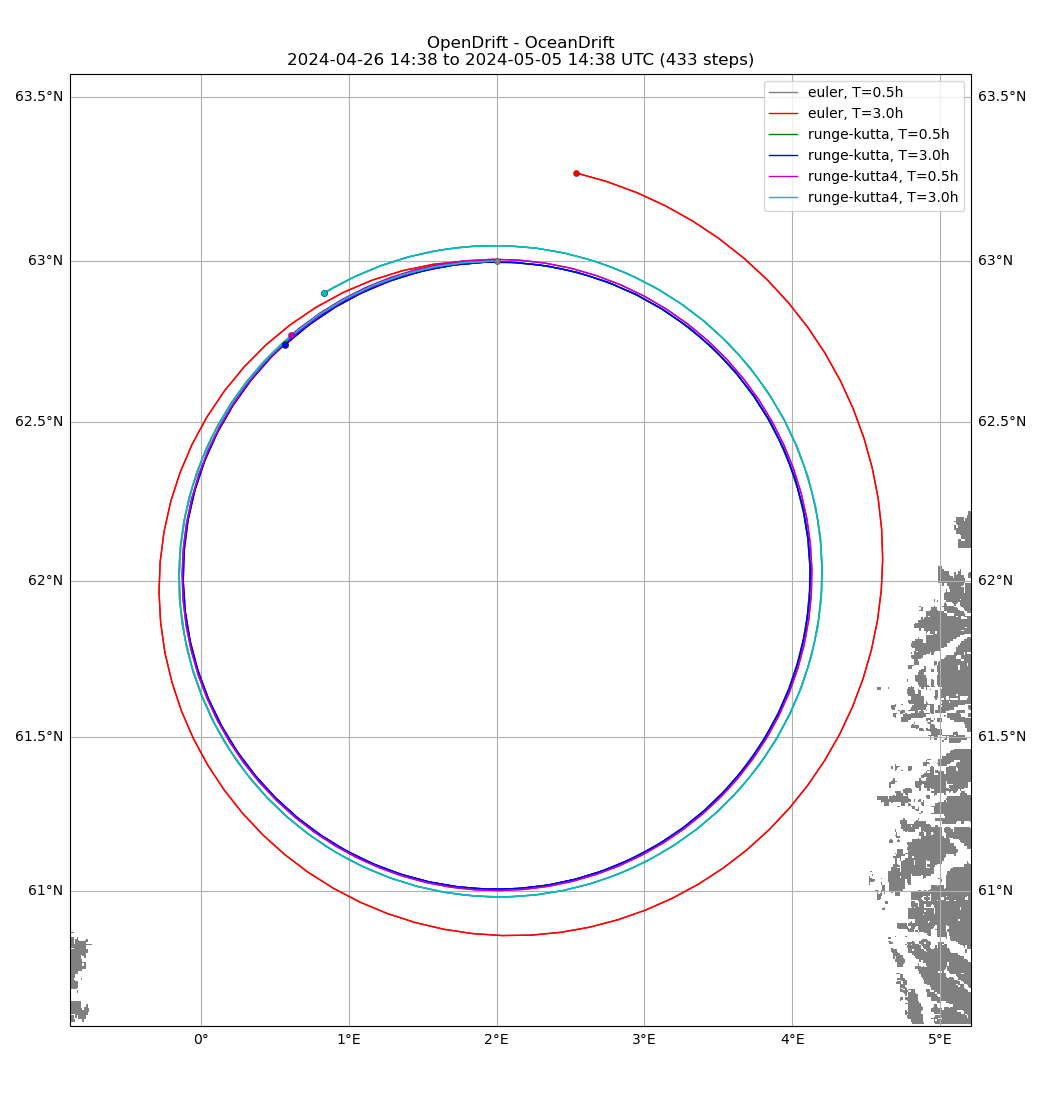
Assuming time step of 1 hour for ArtificialOceanEddy
euler, T=0.5h
euler, T=3.0h
runge-kutta, T=0.5h
runge-kutta, T=3.0h
runge-kutta4, T=0.5h
runge-kutta4, T=3.0h
(<GeoAxes: title={'center': 'OpenDrift - OceanDrift\n2026-03-03 14:15 to 2026-03-12 14:15 UTC (433 steps)'}>, <Figure size 1041.68x1100 with 1 Axes>)
from datetime import datetime, timedelta
from opendrift.readers import reader_ArtificialOceanEddy
from opendrift.models.oceandrift import OceanDrift
fake_eddy = reader_ArtificialOceanEddy.Reader(2, 62)
runs = []
leg = []
for scheme in ['euler', 'runge-kutta', 'runge-kutta4']:
for time_step in [1800, 3600*3]:
leg.append(scheme + ', T=%.1fh' % (time_step/3600.))
print(leg[-1])
o = OceanDrift(loglevel=50)
o.set_config('environment:fallback:land_binary_mask', 0)
o.set_config('drift:advection_scheme', scheme)
o.set_config('drift:vertical_mixing', False)
o.add_reader(fake_eddy)
o.seed_elements(lon=2.0, lat=63.0, time=datetime.utcnow())
o.run(duration=timedelta(days=9), time_step=time_step)
runs.append(o)
runs[0].plot(compare=runs[1:], legend=leg, fast=True, buffer=.3)
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 43.569 seconds)